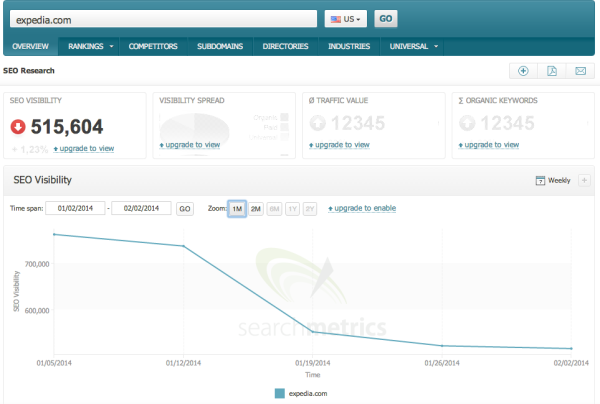
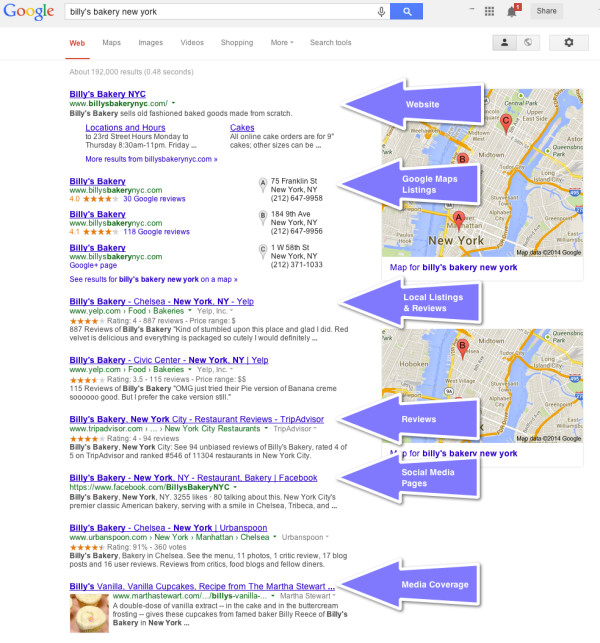
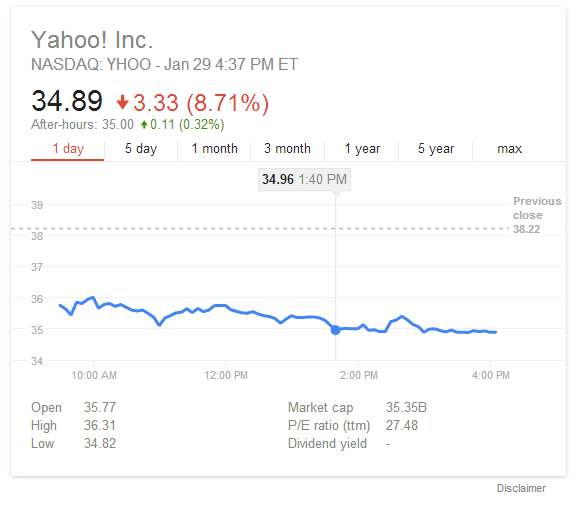
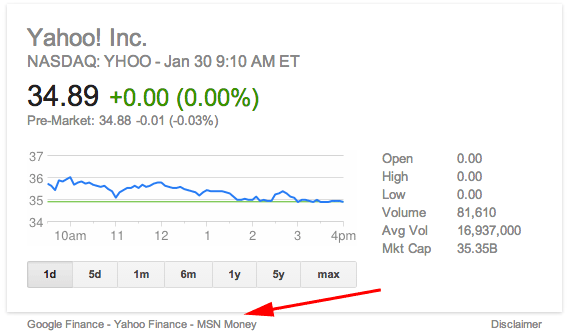
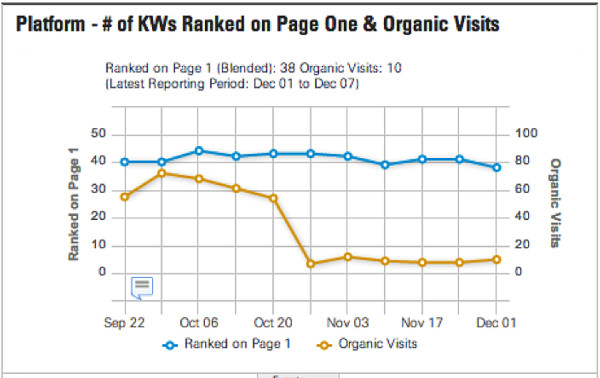
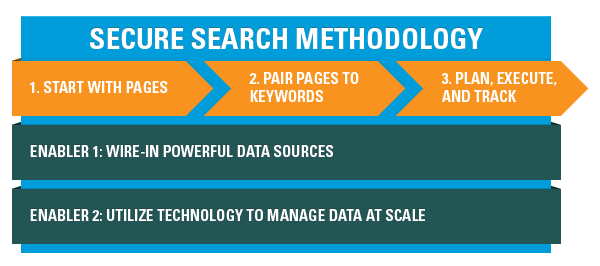
The importance of link quality in SEO cannot be overstated1. Before you begin any link building project within2 SEO, you must be sure you’re pursuing3 links that will not only have an impact
today, but will continue to have a positive impact in the future.
4That means understanding what makes a quality link, and why. Let’s take a look at the elements of link analysis, which are:
- Relevance
- Link Type
- Authority
- Location
- Smell Test
Relevance
Relevance should always be the north star of your link building compass. Without relevance, a link will, at best, be sub-par quality and, at worst, negatively impact your SEO efforts, potentially resulting in a manual penalty from Google, or the algorithmic penalty (filter) Penguin.
Of course, relevance isn’t the only factor worth considering, but it’s certainly the first you should examine. And, as with all elements of a link, relevance needs to be analyzed at both the page and domain level.
The page level should always be strictly relevant — if the link doesn’t make contextual sense on the page, the link will be useless or worse.
Domain to domain relevance should be a goal, as well, although there will be times that the link only makes relevant sense at the page level. A good example of a quality link lacking domain relevance would be a link from the New York Times to, say, a Mom blog. Obviously, the Mom blog would and should be thrilled to have the link, despite the lack of domain relevance.
Link Type
Link type is the second consideration when analyzing a link. This means both the way the link is formed and the manner in which it’s linking, both of which make a difference in link quality.
First, let’s examine the different ways a link can be formed:
• Anchor Text Link. Anchor text is the visible, clickable text of the link. Anchor text links are the most common and best way to increase search ranking for a targeted keyword; although, Penguin will punish over-optimization. The words used as anchor text can include branded, keyword-rich, partial branded, long tail, etc. Variety is extremely important in organic link building.
• Naked URL. A naked URL is when the full path URL used as the anchor text (http://www.example.com/). These are a very natural way to link, although not as powerful as an anchor text link.
• Citation Link. Citation links are the condensed version of a naked URL, e.g., pageonepower.com instead of http://pageonepower.com/. Citation links tend to be more powerful if your web address is the same as your brand name (i.e., Page One Power and pageonepower.com).
• Image Link. An image link is when an image is used as the link — in other words, clicking the image takes you to a new page. These are good for link diversity, as long as the
alt attribute tag is properly utilized (this tag acts as the link’s anchor text, although it’s
slightly less powerful).
• Short Link. A short link is a condensed or shortcut URL that will redirect you to a full URL (e.g.,
http://selnd.com/NqXlw). These links need to be examined to see how they’re redirecting to determine whether they’re passing link equity.
Each of the above methods of linking has its pluses and minuses, and each has an impact on the quality of the link. Now, let’s look at the different manners of linking:
• Direct. A normal, regular link which takes you straight to the intended page. There’s nothing to impede link equity or link quality.
•
Redirect. A redirect is a link that takes you to one page, which then passes you on to another page. This can mean link equity is lost if Google’s crawlers can’t follow the redirect, which will make the link virtually worthless for SEO purposes (outside of referral traffic). Redirected links need to be
checked to see whether they are permanent (301) redirects or temporary (302) redirects — 301s pass link equity, but 302s pass little to no link equity.
•
Site-wide. A
site-wide backlink (video autoplay) is located on every page of the entire linking site. Typically this happens when the link occurs in the footer/sidebar of the site. This can be natural, and Google often counts these as a single link. In some cases, Google may even red flag site-wide links (especially if it’s a pattern), which can bring the wrath of Penguin.
• JavaScript. Often times, JavaScript is used to create drop-down, fly-out or mega menus on a site. Though these are often SEO-friendly, it all depends on how they are coded.
• Nofollow. Nofollow is an html tag which tells Google crawlers to ignore the link. This means the site owner specifically chose not to pass link equity. Google advises using the nofollow tag for paid links or links to websites you don’t specifically trust. There are different arguments about whether or not these have any value, as Google is vague about how they treat them. A few nofollow links are very natural within a site’s backlink profile.
The goal here is to build naturalistic links. You want a variety of naked URL, citation, image and anchor text links. Variety within the anchor text links themselves is essential as well — you should be using a mix of branded terms, partial branded terms, long tail keywords, exact match keywords and synonyms, etc.
As far as the method of linking, you should always strive for direct. Keep an eye on site-wide, redirects and javascript, and be aware of their potential to diminish or hurt your SEO efforts.
Authority
Authority is the next metric you’ll need to measure in order to determine link quality. This was overvalued in the past, often being placed above relevance.
In today’s link building world, authority is still an important link metric. However, if the link isn’t relevant, or the link is created in an artificial/poor manner, then authority won’t be enough to move the needle.
Authority can be measured in a variety of ways, depending on personal preference. There’s the PageRank toolbar, which I don’t recommend as Google only updates it periodically (and it isn’t a great metric to begin with).
Then there’s the toolbar from Moz, which includes the metrics Domain Authority, Page Authority and MozRank. I’ve found this to be the most convenient tool to use as it’s lightweight, accurate and free.
There’s also Alexa Toolbar, of course.
Regardless of how you decide to determine authority, bear in mind that it’s more of a quality check than a determining factor — you want to meet minimum thresholds, not chase the purple dragon of high authority. For link quality, we’ve had much better results acquiring natural links from highly relevant niche sites than chasing after a link from the New York Times.
Make sure to check the authority of the page and the domain, as both will impact link quality.
And, don’t wholly rely on toolbars to tell you a site’s quality, either. Check traffic levels withSEMrush, check out social media engagement and blog comments (if there’s a blog), etc. Check for signs of actual life on the site, and the quality of engagement.
Location
The location of the link on the page is the next factor in link analysis. Where the link is located plays a role in how much link equity is passed. Here’s a sliding scale of link placement, from best to worst:
- In content
- Boxed out of content (e.g. author bio box)
- Sidebar
- Footer
Although old, Rand Fishkin’s article, All Links Are Not Created Equal, still does an outstanding job explaining basic link principles; and, I highly encourage you to take the time to read it.
Now obviously, you can’t always control link placement — in fact, it’s far better to have a link make contextual sense than to be shoehorned in to increase link equity. But for understanding and analyzing links, keep in mind that the location of the link does affect the link’s overall quality.
Smell Test
SEO is in some ways an art as much as it is a science. When analyzing a link, it’s important to look beyond link metrics. The site as a whole needs at least a quick quality analysis.
One thing I’ve learned from doing thousands of quick site analyses is this: don’t be afraid to listen to your instincts.
In link building, I refer to this as the “smell test” — our noses know when a site stinks, sometimes even before we can logically determine it.
Don’t be afraid to listen to your gut, your nose or whatever anatomical part you’d like to metaphorically engage.
More specifically, here’s what I typically look at when performing a quick and dirty smell test:
- Other outbound links on the page and even domain
- Content quality, both page and domain
- Website or brand information
- Contact information
- Date/frequency of blog posts (if there is a blog)
Basically, scan through the site with a critical eye. Do they have a blog? Is it up to date? How’s the content quality? Do they have an in-depth About page? Are they linking out to irrelevant sites? Do they have an address in the contact page? What about a phone number? Who runs the site? What’s their background?
All of these questions will separate the wheat from the chaff — a real website from a thinly veiled spam site.
Once again, this is to make sure your link isn’t in a bad “link neighborhood.” Check the site for quality practices outside of link metrics. Spend enough time scouring the web and you’ll develop a keen sense of site quality, quickly.
Putting it all Together
The point of breaking down and analyzing a link is to better understand a strong link versus a weak link and what separates the two.
If you’re worried about a link, simply check:
- Page and Domain Relevance
- Link type
- Site Authority
- Link Placement
- Website Smell Test
By the end, you’ll have a better understanding of the value of the link, not to mention an idea of the quality of the linking website.
The goal should be good links on sites that make sense, which will continue to have a positive ongoing impact on your SEO efforts.
Opinions expressed in the article are those of the guest author and not necessarily Search Engine Land.
Source: Searchengineland.com